- Modulation is a process in which a message signal or called as modulating signal is merged with a comparatively stronger signal or called as carrier signal for a quite large distance signal transmission.
- In this process , characteristics of a high frequency signal , is changed according to the instantaneous amplitude of the information signal.
- Modulation is used for Long distance transmission. Multiple signals can be transmitted on a single or in a same channel. It also makes signal to become more stable. It promotes noise rejection also.
- Modulation is used for broadcasting both audio and video signals.
- Modulation is used in entire communication industry for all types of communication such as in Mobile, Television, Satellites etc.
TYPES OF MODULATION:
- Amplitude modulation
- Frequency modulation
- Phase modulation
1.AMPLITUDE MODULATION:
Amplitude modulation or just AM is one of the earliest modulation methods that is used in transmitting information over the radio. This technique was devised in the 20th century at a time when Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden were conducting experiments using a radiotelephone in the 1900s. After successful attempts, the modulation technique was established and used in electronic communication.
In Amplitude modulation just we varied the High frequency Carrier signal according to the instantaneous amplitude of the Modulating signal or Message signal.
- The Amplitude modulation is generated through a multiplier.
- Amplitude modulated signal or AM signal has two different side bands called as Upper side band and lower side band.
- All the information sent by the sender are present in two side bands.
- AM Carrier signal has Time-varying Envelop.
- In frequency domain the AM waveform are lower side band is(fc-fm), the Carrier frequency is fc, the upper side band is (fc+fm).
MATHMETICAL EXPRESSION:
We have carrier wave and modulating signal,
→1
m(t) 🡪 modulating signal
c(t) 🡪 carrier wave.
Am and Ac 🡪 are Amplitude of modulating signal and carrier wave respectively in Amplitude modulation. We are superimposing modulating signal into carrier wave and also varying the amplitude of the carrier wave in accordance with the amplitude of the modulating signal and the amplitude-modulated wave Cm(t) will be
Cm(t) = (Ac + Am sin ωmt) sin ωct ……………….. 2
This is the general form of amplitude modulated wave Cm(t) 🡪 is the amplitude-modulated wave.
Where,
A = Ac + Am sin ωmt → is the amplitude of the modulated wave
Sin wct → phase of modulated wave
=
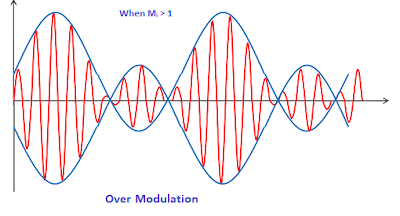
Modulation index is nothing but the ratio between the messege signal amplitude and the carrier signal amplitude.
m=Am/Ac




This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDelete👍
ReplyDelete